What is Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 EV Charger?
What is Level 1 ev charger?
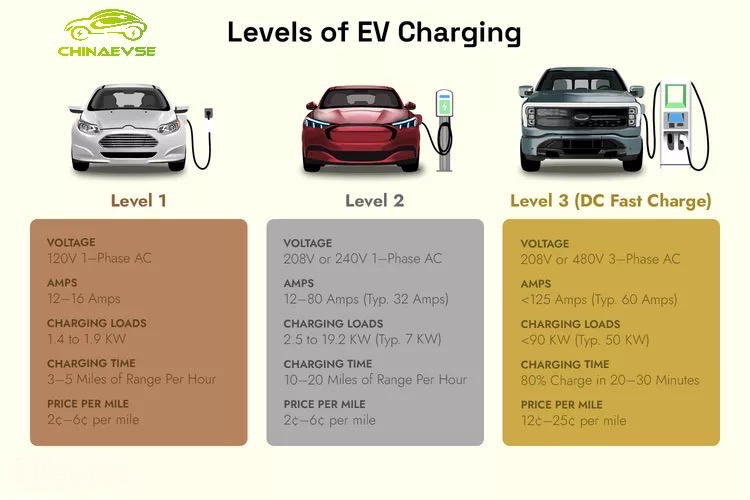
Every EV comes with a free Level 1 charge cable. It’s universally compatible, doesn’t cost anything to install, and plugs into any standard grounded 120-V outlet. Depending on the price of electricity and your EV’s efficiency rating, L1 charging costs 2¢ to 6¢ per mile.
The Level 1 ev charger power rating tops out at 2.4 kW, restoring up to 5 miles per hour charge time, about 40 miles every 8 hours. Since the average driver puts on 37 miles per day, this works out for many people.
The Level 1 ev charger can also work for people whose workplace or school offers Level 1 ev charger points, allowing their EVs to charge all day for the ride home.
Many EV drivers refer to the L Level 1 ev charger cable as an emergency charger or trickle charger because it won’t keep up with long commutes or long weekend drives.
What is Level 2 ev charger?
The Level 2 ev charger runs at higher input voltage, 240 V, and is usually permanently wired to a dedicated 240-V circuit in a garage or driveway. Portable models plug into standard 240-V dryer or welder receptacles, but not all homes have these.
Level 2 ev charger cost $300 to $2,000, depending on brand, power rating, and installation requirements. Subject to the price of electricity and your EV’s efficiency rating, Level 2 ev charger costs 2¢ to 6¢ per mile.
Level 2 ev charger are universally compatible with EVs equipped with the industry-standard SAE J1772 or “J-plug.” You can find public-access L2 chargers in parking garages, parking lots, in front of businesses, and installed for employees and students.
Level 2 ev charger tend to top out at 12 kW, restoring up to 12 miles per hour charge, about 100 miles every 8 hours. For the average driver, putting on 37 miles per day, this only requires about 3 hours of charging.
Still, if you’re on a trip longer than the range of your vehicle, you’re going to need a quick top-up along the way that Level 2 charging can provide.
What is Level 3 ev charger?
Level 3 ev charger are the fastest EV chargers available. They typically run on 480 V or 1,000 V and aren’t typically found at home. They’re being better suited to high-traffic areas, such as highway rest stops and shopping and entertainment districts, where the vehicle can be recharged in less than an hour.
Charging fees might be based on an hourly rate or per kWh. Depending on membership fees and other factors, Level 3 ev charger costs 12¢ to 25¢ per mile.
Level 3 ev charger are not universally compatible and there is no industry standard. Currently, the three main types are Superchargers, SAE CCS (Combined Charging System), and CHAdeMO (a riff on “would you like a cup of tea,” in Japanese).
Superchargers work with certain Tesla models, SAE CCS chargers work with certain European EVs, and CHAdeMO works with certain Asian EVs, though some vehicles and chargers may be cross-compatible with adapters.
Level 3 ev charger generally start at 50 kW and go up from there. The CHAdeMO standard, for example, works up to 400 kW and has a 900-kW version in development. Tesla Superchargers typically charge at 72 kW, but some are capable of up to 250 kW. Such high power is possible because L3 chargers skip the OBC and its limitations, directly DC-charging the battery.
There is one caveat, that high-speed charging is only available up to 80% capacity. After 80%, the BMS throttles the charge rate significantly to protect the battery.
Charger levels compared
Here’s a comparison of Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. Level 3 charging stations:
Electrical output
Level 1: 1.3 kW and 2.4 kW AC current
Level 2: 3kW to under 20kW AC current, output varies by model
Level 3: 50kw to 350kw DC current
Range
Level 1: 5 km (or 3.11 miles) of range per hour of charging; up to 24 hours to fully charge a battery
Level 2: 30 to 50km (20 to 30 miles) of range per hour of charging; overnight full battery charge
Level 3: Up to 20 miles of range per minute; full battery charge in under an hour
Cost
Level 1: Minimal; nozzle cord comes with the EV purchase and EV owners can use an existing outlet
Level 2: $300 to $2,000 per charger, plus the cost of installation
Level 3: ~$10,000 per charger, plus hefty installation fees
Use cases
Level 1: Residential (single-family homes or apartment complexes)
Level 2: Residential, commercial (retail spaces, multi-family complexes, public parking lots); can be used by individual homeowners if a 240V outlet is installed
Level 3: Commercial (for heavy-duty EVs and most passenger EVs )